Blood supply to the cervical system
The cervical system starts at the subclavian artery and ascends through transverse foramen of cervical vertebrae, then continue medially and enter through the foramen magnum, they piece the dura matter and subarachnoid matter and anastomose with each other in pontomedullary junction and continue as the basilar artery on the anterior aspect of the midbrain where it split to posterior cerebral arteries. (split above the third cranial nerves)
Posterior cerebral arteries supply the posterior part of the cerebral hemisphere and a part of the midbrain.
Branches
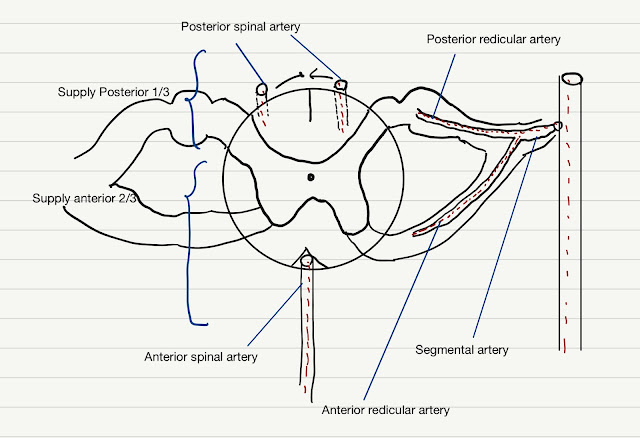
-Anterior spinal artery:
arise from the 2 vertebral arteries in front of the medulla. They anastomose and descend on the anterior median fissure of the spinal cord, supply anterior 2/3 of it.
-Posterior inferior cerebellar artery:
arise from the 2 vertebral arteries and follow the inferior border of the cerebellum and run posteriorly, supply the cerebellum, and also the medulla.
-2 Posterior spinal arteries:
it can arise from the 2 vertebral arteries or indirectly, from the posterior inferior cerebellar arteries, and supply the posterior 1/3 of the spinal cord.
the spinal cord artery system is also reinforced by segmental arteries (arising from the deep cervical artery, intercostal artery, and lumbar artery) which give rise to anterior and posterior radicular arteries.
other arterial reinforcement came from the aorta by "Great radicular artery of Adam" (AdamaKiewicz), it arise usually from the left side of the aorta between T8-L1, in some cases can be risen from the right side, lumbar artery and sometimes can be as 2 segments (arteries) instead of one. It supplies the lower 2/3 of the spinal cord via the anterior spinal artery.
- other branches arise from the basilar artery or sometimes from vertebral arteries are "Anterior Inferior cerebellar arteries", it also supplies the inferior surface of the cerebellum (but on anterior surface) and part of the pons.
- other branches arise from basilar artery are "labyrinthine arteries", it travels a long way along with facial nerve (CN7) and vestibulocochlear nerve (CN8), it enters the middle ear through the internal acoustic meatus, the labyrinthine artery supplies that.
- other branches arise from the basilar artery at the level of the midbrain, "superior cerebellar arteries", it supplies the superior surface of the cerebellum and a part of the midbrain (below the 3rd cranial nerve).
Carotid system:
- The internal carotid artery enters the cranium through the carotid canal, go forward and up through the foramen lacerum to the middle cranial fossa and to the cavernous sinus medial to the anterior clinoid process going up to pierce the dura matter and arachnoid matter. (the pituitary located between the arteries).
- It gives a branch called "ophthalmic artery" which enter the orbital cavity to supply it, it gives few branches:
- Anterior and Posterior ethmoidal arteries
- Supra-trochlear artery
- Supra-orbital artery
- Retinal arteries
- "Posterior communicating artery", which anastomose with the basilar system (on the posterior cerebral arteries) →goes backward
- "Anterior choroidal artery": other branches of the carotid system.
- After giving those branches the internal carotid artery continues and gives 2 terminal branches:
- Anterior cerebral artery goes anterosuperior and anastomoses with the other side by "anterior communicating artery"
- Middle cerebral artery goes laterally
- the anastomose between the posterior and anterior circulation creates the "circle of Willis"






Comments
Post a Comment